I experience severe inflammatory issues after consuming turmeric. It was not the case some years ago when I used to take golden milk as turmeric benefits for joint pain or fatigue until I was diagnosed with Rheumatoid Arthritis. The medication (a disease-modifying anti-inflammatory drug) interacts with my anti-inflammatory herbal remedy.
Turmeric is a perennial herb belonging to the Zingiberaceae family, with a height of approximately 3.5 ft. It is indigenous to Southern Asia, including Pakistan. Curcumin, active ingredient in turmeric, is widely studied for its therapeutic properties. The rhizome of turmeric is used as a spice for flavoring and has medicinal benefits.
Turmeric Benefits
Turmeric is well known for home remedies for Pneumonia, Sore throat, dry throat, sinusitis, cough and cold, ring worms, Psoriasis, Toe-nail fungus, Scabies, digestive issues like nausea, bloated stomach, diarrhea, cramps, pancreatitis. It is a necessary part of food for Rheumatoid Arthritis for centuries. These are important health benefits of Turmeric
- Herbal Medicine and Culinary Use: People in different parts of the world, particularly in Asian countries, use the rhizome of turmeric as an herbal medicine, coloring agent, spice, and food additive from thousands of years.
- Traditional Medical Applications: Many traditional medical schools, including Islamic traditional medicine, Chinese traditional medicine, and Ayurveda, have employed turmeric for various diseases and conditions.
- Digestive Problem Relief: Turmeric addresses digestive problems.
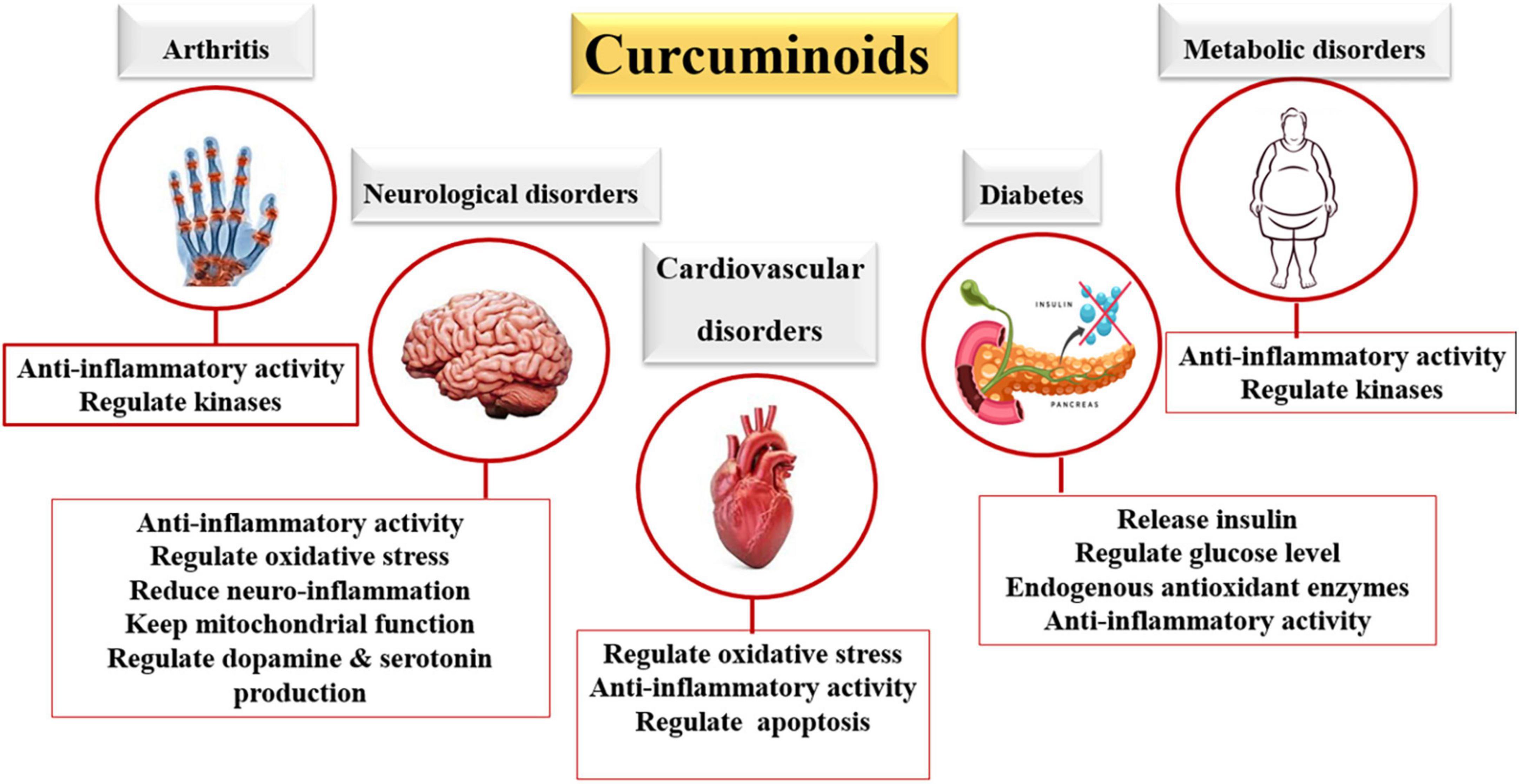
- Protective Effects: It has shown heart, liver and brain protective properties.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Turmeric alleviates inflammation, especially in conditions like arthritis.
- Immune System Enhancement: It enhances the immune system.
- Curcumin’s Properties: Curcumin, a key constituent in turmeric, exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties.
- Obesity and Metabolic Control: Turmeric has potential in controlling obesity and metabolic problems.
- Memory and Mood Improvement: Curcumin improves memory and mood disorders.
- Therapeutic Potential: Preclinical and clinical studies show promising results for curcumin in treating conditions such as metabolic syndrome, liver disease, arthritis, depression, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Harmful effects
Many studies confirm the safety of turmeric, but some side effects also exist. Further research is needed to understand their full implications and potential risk factors.
- Gastrointestinal Effects: Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain in the abdominal region, nausea or constipation. Some individuals may experience sudden and intense episodes of heat and sweating.
- Toxicity and Carcinogenic Potential: High doses of curcumin can lead to vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, rashes, and yellow stools. Curcumin can cause DNA damage at both mitochondrial and nuclear levels, indicating potential carcinogenic effects. In studies conducted on mice, turmeric showed the potential for causing cancer after long-term exposure.
- Enzyme Inhibition and Metabolism Interference: Curcumin can inhibit the activities of important drug-metabolizing enzymes. Blockage of drug-metabolizing enzymes can lead to the buildup of xenobiotics, potentially causing toxicity. Turmeric may chelate iron, affecting its metabolism and distribution in the body. In a study, subjects receiving curcumin reported increased levels of serum alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase.
- Gallbladder Problems: Turmeric may stimulate the production of bile, which can be problematic for individuals with gallbladder issues or those who have gallstones. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before consuming turmeric if you have a history of gallbladder problems.
- Interactions with Medications: Turmeric can interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and drugs metabolized by the liver. These interactions can affect the effectiveness and safety of the medications, so it is important to consult a healthcare professional before using turmeric alongside any medications.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and lactating mothers should avoid high doses of turmeric supplements due to the lack of sufficient safety data.
- Allergic Reactions: Turmeric can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Symptoms may include skin rash, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. It is important to seek medical attention if any allergic reaction occurs.
- Interference with Blood Clotting: Turmeric has blood-thinning properties, which can interfere with blood clotting. This may pose risks for individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Excessive consumption of turmeric in such cases can increase the risk of bleeding or bruising
conclusion
Turmeric can potentially prevent and treat various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, obesity, allergies, asthma, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. Compared to other medications, it is a cost-effective and safe natural product. But it may cause issues if patients are already taking medications, have bleeding disorders, or are allergic to turmeric. High doses of turmeric may also affect pregnancy and lactation. By actively exploring these areas, we can gain a deeper understanding of curcumin’s therapeutic potential and ensure its safe and effective utilization in the future.
Note: images courtesy of Canva.com.